Rome Metro - Line C
The capital’s new metro line: a blend of sustainability, culture and innovation

A project that builds the future
The Rome Metro Line C project will provide Rome with a cutting-edge infrastructure in the mobility sector.
Building a similar work represents an engineering challenge. Rome's soil is due to its anthropic features unique: a city filled with life, founded over 3,000 years ago. In it, you can see what is left of various civilizations, eras, and generations, which one after the other have made its history, our heritage. Building Line C meant meeting a fundamental work, both for the present and the future, while respecting the past.
The Line and its stations
The Line C crosses Rome, connecting the city from its south-eastern area to its north-western one, the city's suburbs to its historical centre. It crosses historical Roman neighbourhoods, reaching Piazzale Clodio. 26 km in length, 17 of these underground and 9 above ground with a total of 29 stations, from the Monte Compatri/Pantano station to the Clodio/Mazzini one.
The project's construction has followed a functional sectional approach. The section that from the terminal at Pantano in the Monte Compatri municipality, reaches San Giovanni, has already been completed: 19 km of metro line, 22 stations and 1 depot are all already fully operating.
The next stations to be connected will be Porta Metronia, Colosseo - Fori Imperiali and Venezia, in Rome's city centre, all currently being built; while the Chiesa Nuova, San Pietro, Ottaviano and Clodio/Mazzini stops are currently being designed.
The project also foresees 4 interconnection stations: San Giovanni and Ottaviano stations (with Line A ); Colosseo stop (with Line B), Pigneto stop (with local railways FL1/FL3).
The line’s most unique feature is its archaeo-stations, which boast fully fledged museums integrated into the stations themselves, connecting the key cultural areas of the city by means of a route adorned with the archaeological finds unearthed during excavations: in addition to San Giovanni, which is now operational, Porta Metronia, Colosseo/Fori Imperiali and Venezia will also be archaeo-stations.
How is a station of Rome's Metro C excavated? How Venezia Station is built – Geopop/Webuild
Metropolitana di Roma, Linea C - Italia
How We build the future
To build a large complex infrastructure in such a unique territory, the most appropriate excavation and construction techniques for the context were used.
Different excavation techniques
Tunnel excavations were built using two methods: traditional excavation and mechanized excavation with a TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine). Considering the historical and structural situation of the area, the choice of one technique over the another, was attentively considered, based on engineering and geological needs.
Four TBMs (of the EPB - Earth Pressure Balance type) were used for the mechanised excavation. TBMs are technologically advanced excavation machines that support the excavation front and line the tunnel, so that it is ready to be equipped and to function, saving considerable amounts of time.
Crosswalls and freezing
During works, various cutting-edge techniques were used to merge effectiveness and safety during excavation works with needs relating to the historical and monumental context, where the project is being built.
The crosswalls technique, used for the very first time in Rome and Italy, allow to carry out excavation works, safeguarding the city's historical and artistic heritage. They are concrete non reinforced walls, perpendicular to the perimeter walls. Once their supporting function has been carried out, they will be demolished as the excavation works of the station proceed.
Another technique used was freezing: a consolidation technique of the soil that foresees building a protective wall of frozen soil within which the excavation works for the tunnel and its lining are carried out. This technique is the most appropriate in urban environments with soil that is permeable, as it ensures the greatest safety level possible.
Rome Metro - Line C project infographic - Webuild
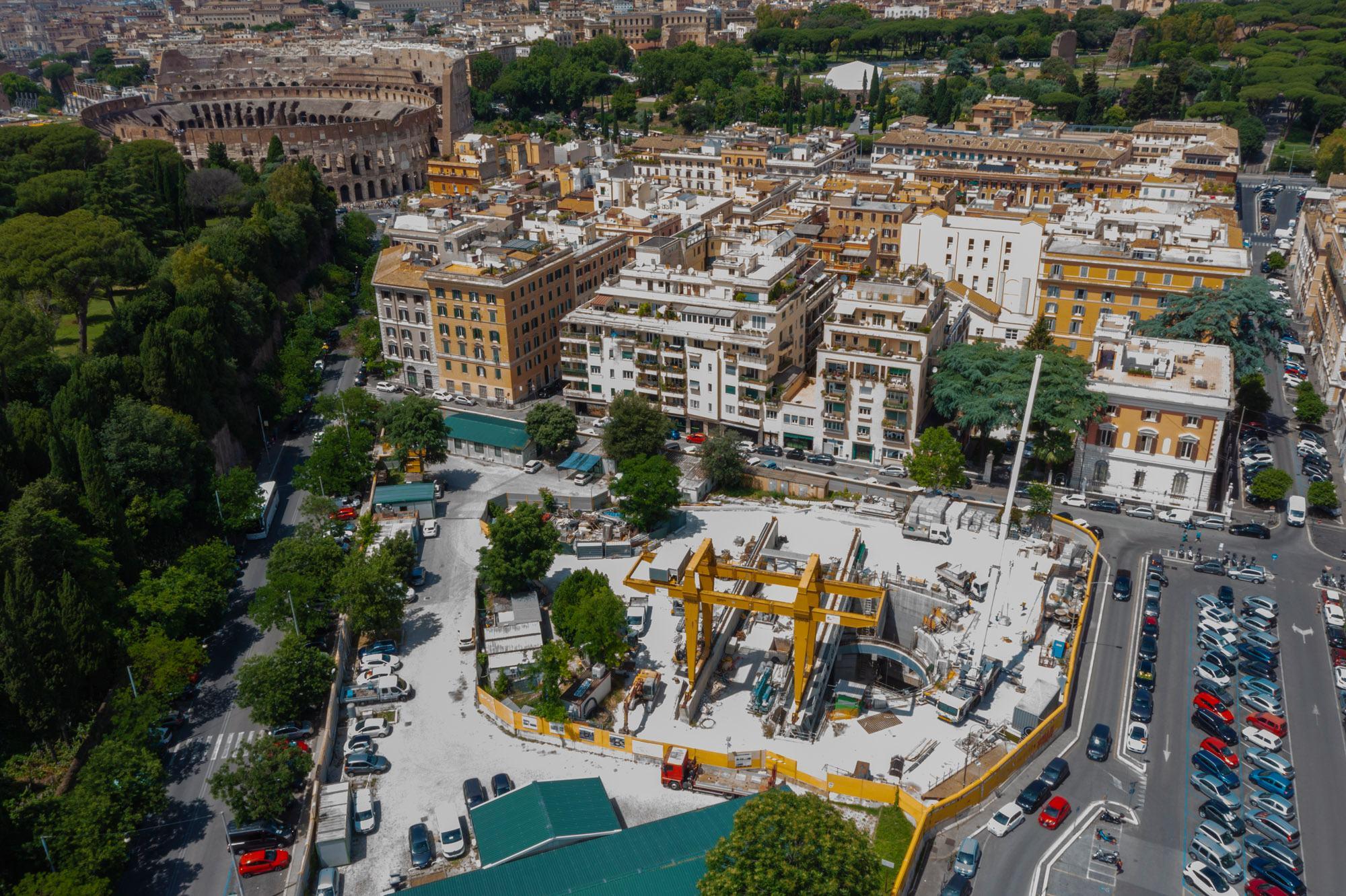

Technical data
Data pertaining to the main Monte Compatri/Pantano - Clodio-Mazzini section of the line
+ + +
m3 of concrete
+ + +
tons of steel
+ + +
m3 of underground excavations
Building the future while valuing the past
The engineering challenge to build Line C of Rome's Metro follows the same path of another challenge: safeguarding and valuing the city's cultural heritage, as its historical centre, since 1980, has been acknowledged as part of the World Heritage of UNESCO.
The project changes the paradigm that is often found in Rome's other construction works: the past is not an obstacle, but instead something of value, and the project was a unique occasion to bring greater value to unique historical pieces.
Archaeological Heritage Safeguarding Studies
Construction works to build Line C stations were carried out in constant collaboration with the Italian State's and Rome's supervisory bodies. This ongoing and virtuous exchange allowed the identification of numerous findings and to update the archaeological maps in areas that until this moment had not been greatly investigated.
29 sites with archaeological mode were investigated along the Pantano - San Giovanni route. In the central area, along the via Sannio - Piazza Venezia - piazzale Clodio/Mazzini route, a further 22 construction sites with archaeological excavation mode were open for preventive investigation purposes.
With Rome's Supervisory Body, a document was drawn-up with a specific procedure to allow works to proceed at full speed while also safeguarding the soil-hidden archaeological findings. This document is called “Prontuario delle indagini archeologiche di seconda fase” and it is the first document of this kind to be drawn-up in Italy.
Archaeological top-down
During this rich collaboration a new archaeological excavation technique was detailed called "top-down". This innovative excavation technique was created to carry out the archaeological excavations in open air up to a depth of 18-20 metres from the surface with the construction need to limit the construction site areas.
The technique in fact foresees building, going down in the ground, intermediate floors to ensure the possibility of carrying out archaeological excavations concomitantly with the construction works of the flooring levels, with benefits in terms of optimizing construction times and area occupation ones with regard to the construction sites.
Excavations saw the detection of 500,000 findings, 4,000 solely in the San Giovanni station, which was made into a museum-station with exposition areas with findings and informative material set on walls. A solution that has become a model even for the other stations being built. It received the ROMARCHITETTURA 6 Award, for the set-up of San Giovanni museum-station, awarded to Metro C in 2017 by IN / ARCH Lazio.
Constant monitoring
Along its route, Line C interacts with historic buildings and monuments of great value located on the surface, such as the Colosseum, the Basilica of Maxentius or the Vittoriano. To ensure the preservation of this heritage, an study of the interaction with monuments was developed, which involved 13 sites and 40 historic buildings. At the same time, constant monitoring of the buildings was started, in order to verify the correspondence between the design forecasts and the acquired data and measurements. In fact, an agreement has been stipulated with the Department of Geotechnical and Structural Engineering at "La Sapienza" University for structural analyses of the soil from which 2D and 3D models have been developed.
Monitoring continues during construction, through analysis models that allow for further study of the project. An ad hoc monitoring system which makes use of an SDD platform was implemented for this purpose, specially calibrated and developed for Line C. Process automation allows comparison with previously collected data, ensuring reliability and speed.
Art historian Claudio Strinati glides along the route of Line C, demonstrating how the same intersects with Ancient Rome's locations and the Baroque era’s of downtown Rome.
Two-thousand metres, two-thousand steps, one life. Claudio Strinati's Journey inside the Metro C's construction sites
Metropolitana di Roma, Linea C, Stazione Colosseo - Webuild
Building a future of innovation, development, and sustainability
Driverless technology
Line C of Rome's Metro runs on innovation. The fact that the trains are driverless certainly brings added technological value to the work, and this technology is already being used in every station that is already in operation. Driverless technology (Integral Automation System) manages all vehicle fucntions remotely, without a driver on board. All operations are managed remotely and centrally in a location called "Direzione Centrale Operativa (Central Operations Hub) that is both the heart and brain of this system, and that is located at the Graniti Depot in an area of approximately 210,000 m2. From this Central Hub to the trains, another small record must also be mentioned: the driverless trains of Line C are Europe's longest highly automated trains, measuring 109.4 metres in length.
Line C's benefits
Line C represents a development opportunity starting from its construction. Beginning from economic development: from when works began, the project engaged approximately 1,500 suppliers, with a supply chain all set in Italy: approximately 98% of the companies that worked on the project are Italian.
The works allows Rome to be more accessible, reducing traffic from the south-western suburbs to the city centre, fully integrating with the public transport system and creating a real "network effect" for Rome's mobility.
Line C will especially allow to transport up to 800,000 daily passengers, in other words potentially 24,000 users every hour in each direction.
The sustainable line for urban regeneration
When underground works are finished, the areas above ground interested by the construction sites will be handed gradually back to the community, restored and redesigned. And the external arrangements of both stations and shafts are designed to create places where people can all meet.
Line C is a line that builds sustainability. During works, urban green spaces were greatly considered: the project in fact has built approximately 98,000 m2 of green areas and over 4,300 new trees were planted. The line will hugely impact future sustainability. It will reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 310,000 tons every year.
Some of the solutions used to build Line C, could become a reference engineering benchmark for works to be built in areas with many historical and cultural buildings. Line C is work that for many aspects is already building the future.

Sustainability KPIs
+ + +
tons/year of CO2 emissions
+ + +
m3 of archaeological excavations
+ + +
passengers/day (maximum capacity)
+ + +
Ore di trasporto privato all’anno
Venezia Station, a station in the very heart of Rome
Venezia station is located in the historic, cultural, tourist and political heart of Rome, surrounded by unique monuments (the Vittoriano, Palazzo Venezia, the Palazzo delle Assicurazioni Generali, the Chiesa di Santa Maria di Loreto) in an area rich in archaeological finds.
Building a subway station in this area, digging deep while keeping the surrounding treasures intact and maintaining the role of central link to the Piazza, is a unique engineering challenge. At the same time it is an opportunity to reach depths never before explored and enhance the archaeological heritage.
The station is configured as a single work that is integrated with the urban context and the museums, an important junction in the capital’s transport system. A new way to bring together culture, innovation and sustainability.
The new Museum Centre
Venezia station will develop eight levels, of which 6 underground, connected by 27 escalators, 6 lifts and 110- metre platforms. There will be three direct accesses to the square serving the three museum areas:
- system for Palazzo Venezia via two escalators, a fixed staircase and an elevator;
- system for the Ateneo di Adriano and the Fori Imperiali, via two escalators, a fixed staircase and a glass elevator;
- system for the Vittoriano, via an escalator and a fixed staircase.
Thanks to its strategic position, Venezia station will also be a connection hub between the surrounding museum complexes. Once they reach the first underground level, travellers will be able to directly access the museum areas of Palazzo Venezia, the remains of the Athenaeum of Hadrian, the Archaeological Park of the Imperial Forums and the Vittoriano..
Metropolitana di Roma Linea C, Stazione Venezia: le fasi di realizzazione
Line C Rome Metro - Venezia Station - First macrophase completed
Venice Station, the construction of a unique underground
Rome Metro Line C, Venezia Station: the hydro-milling machine's journey
Line C of the Rome Metro, Piazza Venezia Station
Venezia Station: a unique engineering challenge
Line C of the Rome Metro - Venezia Station
Colosseo - Fori Imperiali, the station of wells
During the second phase of archaeological excavations where the Colosseo - Fori Imperiali station will be built, many materials and finds emerged in an excellent state of conservation, evidence of the extraordinary continuity of life from the archaic age to the medieval age in the valley area of the Colosseum.
The Colosseum Archaeological Park therefore requested that a specific installation be provided at the end of the second phase archaeological excavations. The installation was designed in collaboration with the Faculty of Architecture at the University of Rome "La Sapienza" and involves the repositioning of a part of the ancient structures inside the station and the reproduction of some of the wells found during the excavations.
Metropolitana di Roma, Linea C, Infografica Stazione Colosseo-Fori Imperiali - Webuild
3D video of the new Colosseo-Fori Imperiali station
A barracks at Porta Metronia
During the excavations for the Porta Metronia station a discovery was made which in terms of importance and state of conservation is among the most extraordinary in Rome in recent years. It is a barracks dating back to the time of emperor Hadrian.
The remains of the walls and floors allow us to imagine the entire construction: 39 rooms along a central corridor, according to a recurring pattern in the quarters of the barracks of the Roman world. Near the barracks, a domus was also found which was called the "Domus del Comandante". On the floor of these buildings mosaics in excellent condition were found.
To safeguard the finds in this case as well, a project has been envisaged to enhance them with a special installation. To do this without compromising the progress of the work, it was decided that all the finds would be removed, restored and then put back in their original location.
Metropolitana di Roma, Linea C, Infografica Stazione Porta Metronia - Webuild